Written by: Khairul Haqeem, Journalist, AOPG.
Traditional Financial Institutions or FIs are increasingly thinking about how to incorporate digital assets into their operations as the cryptocurrency market continues to develop. The Crypto Maturity Model (CMM) serves as a guide for these businesses as they assess the cryptocurrency’s market potential, tackle compliance and regulation issues, and develop cryptocurrency-based products.
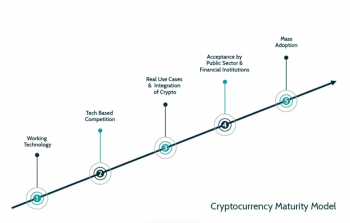
Good times are ahead for traditional FIs as they begin to incorporate cryptocurrency into their operations. The CMM offers a guide for these institutions to assess the market potential of cryptocurrency, navigate compliance and regulation issues, and develop cryptocurrency-based products. The CMM is divided into four stages: Discovery, development, implementation, and refinement, as illustrated below:

Stage 0: The focus of conventional banks should be on educating and strategising for those at the bottom of the pyramid. This includes defining the institution’s risk appetite and developing compliance processes, as well as identifying important stakeholders across numerous functions and assigning an executive to lead the drive. Considerable consideration must also be given to the extent to which the FIs are now exposed to the cryptocurrency market and the associated risk. FIs may benefit from instructional information, social media channels, online platforms and in-person gatherings to learn as much as possible about the cryptocurrency industry.
Stage 1: Once an FI is comfortable working with cryptocurrency organisations, it may go on to the next phase and start selling synthetic cryptocurrency commodities. With these products, investors may have access to the cryptocurrency market without the financial institution having to hold any cryptocurrency. BlackRock’s Bitcoin private trust and bitcoin exchange-traded funds are two examples of synthetic cryptocurrency products. By providing investors with these instruments, FIs may facilitate their participation in the cryptocurrency markets while limiting their exposure to potential losses.
Stage 2: This paves the way for traditional banks to start providing bitcoin firms with more advanced goods and services, beyond simply basic assistance. An example of this is using a decentralised finance (DeFi) platform, which is a digital network that uses smart contracts and cryptocurrency to provide financial services directly to its users without the need for an intermediary. There are a number of examples of financial organisations accepting cryptocurrencies as payment, including Apple Pay’s cooperation with Circle, which enables users to make purchases using the USDC stablecoin, and JP Morgan’s creation of the JPM Coin, which may be used in commercial transactions.
Stage 3: The third phase involves traditional FIs facilitating cryptocurrency deposits, providing direct access to cryptocurrency marketplaces, and maybe even storing cryptocurrency on behalf of consumers. This can only be achieved by building up the appropriate infrastructure and forging strategic alliances with crypto-native companies that can contribute crucial knowledge in areas such as security and compliance.
Stage 4: In the final phase, FIs will be able to provide cryptocurrency users with a wider range of products and services beyond simple deposit and withdrawal options. Participating in DeFi platforms, making payments in bitcoin, and finding other creative applications for digital assets are all possibilities. Now that we’ve reached this point, banks have completely embraced the crypto realm and may provide a variety of crypto-related services to fulfil the varied demands of their consumers.
The CMM provides a framework for FIs to integrate cryptocurrencies in a methodical and progressive manner, testing and refining their services at each level. FIs may use the information gleaned from public blockchains to determine which cryptocurrency services are most applicable to their clientele, given the necessary resources and strategic alliances. In the end, it is all up to the FIs to instil the tenacity to remain competitive within the digitalised utopia we live in today.
 (0)
(0) (0)
(0)Archive
- October 2024(44)
- September 2024(94)
- August 2024(100)
- July 2024(99)
- June 2024(126)
- May 2024(155)
- April 2024(123)
- March 2024(112)
- February 2024(109)
- January 2024(95)
- December 2023(56)
- November 2023(86)
- October 2023(97)
- September 2023(89)
- August 2023(101)
- July 2023(104)
- June 2023(113)
- May 2023(103)
- April 2023(93)
- March 2023(129)
- February 2023(77)
- January 2023(91)
- December 2022(90)
- November 2022(125)
- October 2022(117)
- September 2022(137)
- August 2022(119)
- July 2022(99)
- June 2022(128)
- May 2022(112)
- April 2022(108)
- March 2022(121)
- February 2022(93)
- January 2022(110)
- December 2021(92)
- November 2021(107)
- October 2021(101)
- September 2021(81)
- August 2021(74)
- July 2021(78)
- June 2021(92)
- May 2021(67)
- April 2021(79)
- March 2021(79)
- February 2021(58)
- January 2021(55)
- December 2020(56)
- November 2020(59)
- October 2020(78)
- September 2020(72)
- August 2020(64)
- July 2020(71)
- June 2020(74)
- May 2020(50)
- April 2020(71)
- March 2020(71)
- February 2020(58)
- January 2020(62)
- December 2019(57)
- November 2019(64)
- October 2019(25)
- September 2019(24)
- August 2019(14)
- July 2019(23)
- June 2019(54)
- May 2019(82)
- April 2019(76)
- March 2019(71)
- February 2019(67)
- January 2019(75)
- December 2018(44)
- November 2018(47)
- October 2018(74)
- September 2018(54)
- August 2018(61)
- July 2018(72)
- June 2018(62)
- May 2018(62)
- April 2018(73)
- March 2018(76)
- February 2018(8)
- January 2018(7)
- December 2017(6)
- November 2017(8)
- October 2017(3)
- September 2017(4)
- August 2017(4)
- July 2017(2)
- June 2017(5)
- May 2017(6)
- April 2017(11)
- March 2017(8)
- February 2017(16)
- January 2017(10)
- December 2016(12)
- November 2016(20)
- October 2016(7)
- September 2016(102)
- August 2016(168)
- July 2016(141)
- June 2016(149)
- May 2016(117)
- April 2016(59)
- March 2016(85)
- February 2016(153)
- December 2015(150)
