
Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. today announced the development of network control technology that can securely operate IoT devices installed on-site.
Sensors, manufacturing equipment, and other IoT devices connected to networks in on-site environments such as factories lack the capability for authentication or virus checking, leaving them open to malware attacks that result in stoppages in factory operations. This is a global problem, and existing anti-virus software often cannot be installed in IoT devices due to CPU and memory capacity restrictions, and many existing devices are exposed to threats from cyberattacks.
Fujitsu Laboratories has now developed technology that analyzes and manages the interconnectivity between IoT devices and network devices, based on operating information collected in gateways, responding to successive changes in network structure to identify the communications of IoT devices behaving suspiciously. In addition, Fujitsu Laboratories developed technology to efficiently control communication blocks. If an IoT device infected with malware were to attack other devices, for example, these technologies could detect that communication by comparing ordinary communication routes, based on the relationships of connections recorded in the gateways, with the actual communication routes. Moreover, by restricting the most appropriate network device managed by the gateway, the impact of the cyberattack can be minimized.
Fujitsu Laboratories aims to commercialize these technologies during fiscal 2018 as part of the gateway functionality of the Fujitsu Network Virtuora series of network products, offered by Fujitsu Limited.
Development Background
Recent years have seen an increasing degree of IoT adoption in a variety of industrial fields, and as IoT devices, such as sensors and manufacturing equipment, have been connected to the network, cases of these IoT devices being damaged by malware attacks have occurred worldwide. This has created an urgent need for security countermeasures for IoT devices.
In many cases, however, IoT devices do not support anti-virus software due to CPU, memory, or OS restrictions, and even if anti-virus software is deployed, often software updates that require the device to be rebooted are not executed as the IoT device cannot be stopped while in operation. Due to these factors, the current situation is that many IoT devices are operating with insufficient security measures.
Issues
In light of these problems, various consortiums and network device vendors have proposed measures using gateways to separate the network the IoT devices are connected to from the networks ordinary devices, such as PCs and servers, are connected to (Figure 1). This means that the gateway can protect the devices from cyberattacks from outside networks, but because cyberattacks can be conducted without going through the gateway if a devices infected with malware is connected inside the network the IoT devices are connected to, it was not possible to protect them from cyberattacks from infected devices.
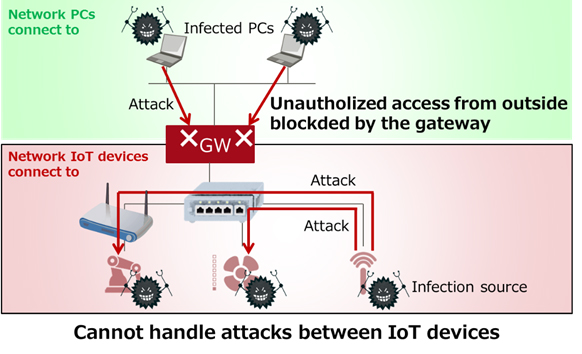
Figure 1: Existing technology: Network separation by a gateway
About the Newly Developed Technology
Now, Fujitsu Laboratories has developed technology that can collect operating information about IoT devices and network devices from gateway devices, deduce the topology of the network the IoT devices are connected to, and appropriately control the network devices based on this information (Figure 2). With this technology, IoT devices communicating along routes not accounted for in the topology can be treated as unauthorized devices, enabling the technology to minimize the impact of cyberattacks by making those IoT devices unable to communicate with other IoT devices.
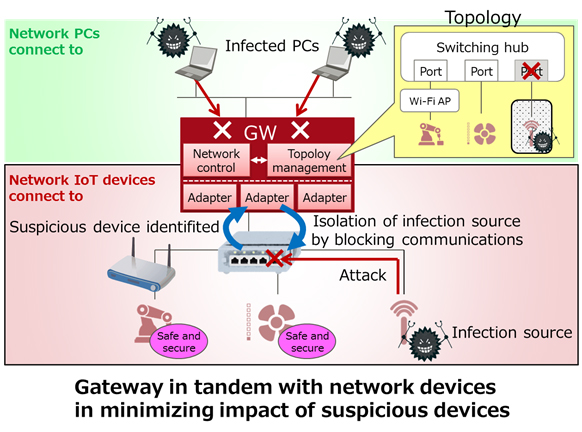
Figure 2: Newly developed method
Features of the Newly Developed Technology
1. Topology management technology supporting devices with a variety of interfaces
This technology collects information from IoT devices and network devices about adjacent devices in a variety of formats, and then deduces the topology of the entire IoT network as it changes in real time. Because the different devices use a variety of interfaces having respective communication methods and data formats, this topology deduction is enabled by converting them all to a standardized interface in the gateway. With this technology, when IoT devices request an authorized communication route, the technology can collect the actual communication route from the network devices, discovering both unauthorized communications generated by cyberattacks and other issues, as well as the suspicious IoT devices that caused them, by comparing the authorized route with the actual route.
2. Network control technology that blocks communications from suspicious devices
Gateways can block communications between suspicious devices and other devices by controlling the network devices along the route using topology information. Because some devices use wireless, rather than wired connections, it is essential to control the appropriate network device, in a situation where communication pathways change moment to moment, and sometimes communications stop altogether. With this technology, it is possible to block communications by suspicious devices while minimizing the impact on communications of ordinary devices by selecting network devices while taking into consideration changes in topology and device status, and controlling those network devices per the connected device or a group of devices.
Effects
In a simulation using fake malware, Fujitsu Laboratories operated gateways equipped with this technology in coordination with existing network devices, and confirmed that this technology could block communications from suspicious devices. The results showed that this technology could minimize the impact of cyberattacks when installed in gateways.
With this technology, it will be possible to provide secure operations using existing setups, without exchanging or deploying new IoT devices with security countermeasures in sites such as factories, which require the continued operation of production equipment with long service lifespans.
 (0)
(0) (0)
(0)Archive
- October 2024(44)
- September 2024(94)
- August 2024(100)
- July 2024(99)
- June 2024(126)
- May 2024(155)
- April 2024(123)
- March 2024(112)
- February 2024(109)
- January 2024(95)
- December 2023(56)
- November 2023(86)
- October 2023(97)
- September 2023(89)
- August 2023(101)
- July 2023(104)
- June 2023(113)
- May 2023(103)
- April 2023(93)
- March 2023(129)
- February 2023(77)
- January 2023(91)
- December 2022(90)
- November 2022(125)
- October 2022(117)
- September 2022(137)
- August 2022(119)
- July 2022(99)
- June 2022(128)
- May 2022(112)
- April 2022(108)
- March 2022(121)
- February 2022(93)
- January 2022(110)
- December 2021(92)
- November 2021(107)
- October 2021(101)
- September 2021(81)
- August 2021(74)
- July 2021(78)
- June 2021(92)
- May 2021(67)
- April 2021(79)
- March 2021(79)
- February 2021(58)
- January 2021(55)
- December 2020(56)
- November 2020(59)
- October 2020(78)
- September 2020(72)
- August 2020(64)
- July 2020(71)
- June 2020(74)
- May 2020(50)
- April 2020(71)
- March 2020(71)
- February 2020(58)
- January 2020(62)
- December 2019(57)
- November 2019(64)
- October 2019(25)
- September 2019(24)
- August 2019(14)
- July 2019(23)
- June 2019(54)
- May 2019(82)
- April 2019(76)
- March 2019(71)
- February 2019(67)
- January 2019(75)
- December 2018(44)
- November 2018(47)
- October 2018(74)
- September 2018(54)
- August 2018(61)
- July 2018(72)
- June 2018(62)
- May 2018(62)
- April 2018(73)
- March 2018(76)
- February 2018(8)
- January 2018(7)
- December 2017(6)
- November 2017(8)
- October 2017(3)
- September 2017(4)
- August 2017(4)
- July 2017(2)
- June 2017(5)
- May 2017(6)
- April 2017(11)
- March 2017(8)
- February 2017(16)
- January 2017(10)
- December 2016(12)
- November 2016(20)
- October 2016(7)
- September 2016(102)
- August 2016(168)
- July 2016(141)
- June 2016(149)
- May 2016(117)
- April 2016(59)
- March 2016(85)
- February 2016(153)
- December 2015(150)
