
Written By: Xiang Lee, Wireless Product Manager, Keysight Technologies

Wi-Fi 7 represents a significant leap in wireless technology. It is engineered to triple the speeds of its predecessor, Wi-Fi 6, supporting a vast array of connected devices, from smart home systems to industrial IoT applications. The transformative power of this innovation lies in its ability to handle multiple high-bandwidth applications simultaneously.
All these technical advancements will drastically increase network complexity, which will lead to more challenges for tests and measurements. Wi-Fi clients and access point manufacturers need a solution that is capable of testing Wi-Fi 7 standards within complex network conditions.
Advancements in Wi-Fi 7 for Enhanced Connectivity
Previous Wi-Fi technologies relied on a maximum of 160 MHz channels at 5GHz, as seen in Figure 1. This limits its ability to support a higher amount of IoT devices in the network. Wi-Fi 7 raises that limit by doubling the channel bandwidth to 320 MHz and adding the 6 GHz band.
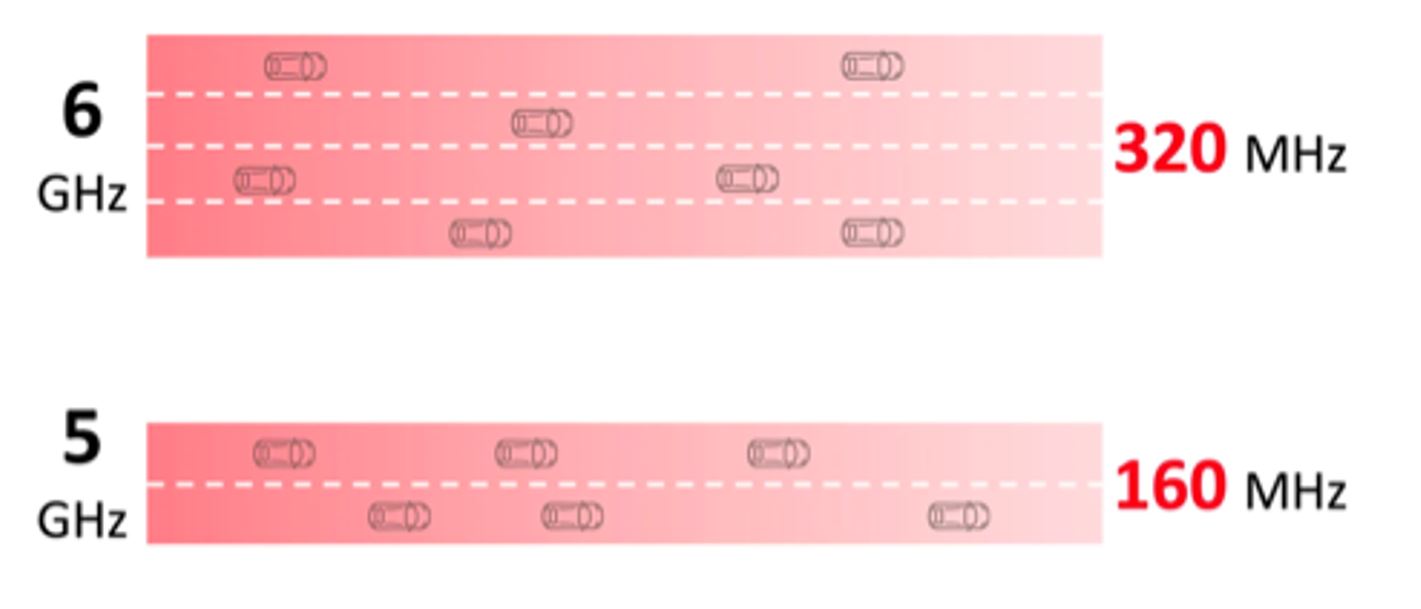
Fig. 1. Wi-Fi 7’s maximum channel bandwidth in the 6 GHz band versus the 5 GHz band of Wi-Fi 6
In addition, Wi-Fi 7 employs 12-bit 4096 modulation instead of 10-bit 1024 modulation from Wi-Fi 6, as shown in Figure 2. For the first time, Wi-Fi will support Multi-Link Operation (MLO) which means devices can use all available bands and channels to transmit data simultaneously rather than relying on a single-channel operation, as shown in Figure 3. All these features enable Wi-Fi 7 to improve speed, latency, and capacity.
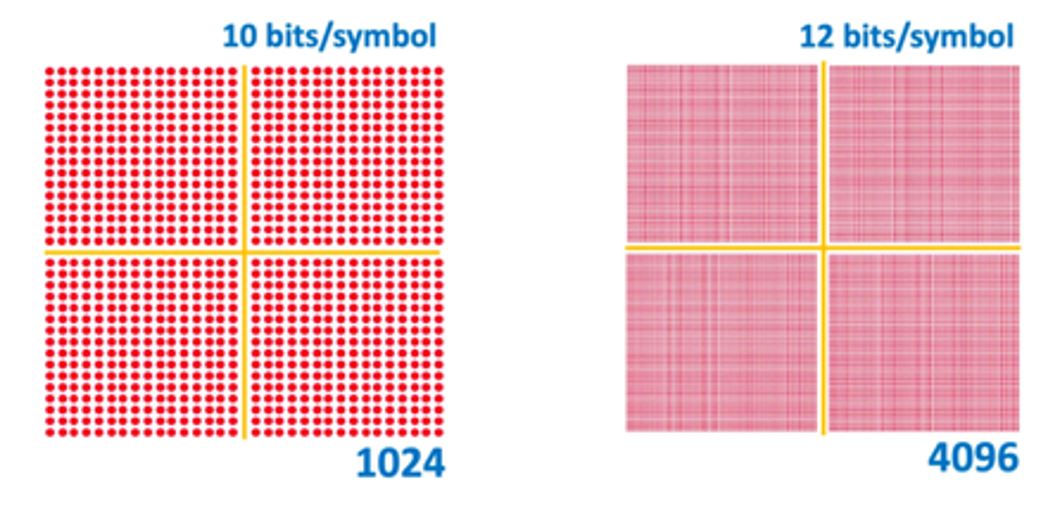
Fig. 2. Wi-Fi 6 1024 QAM modulation scheme vs. Wi-Fi 7 4096 QAM
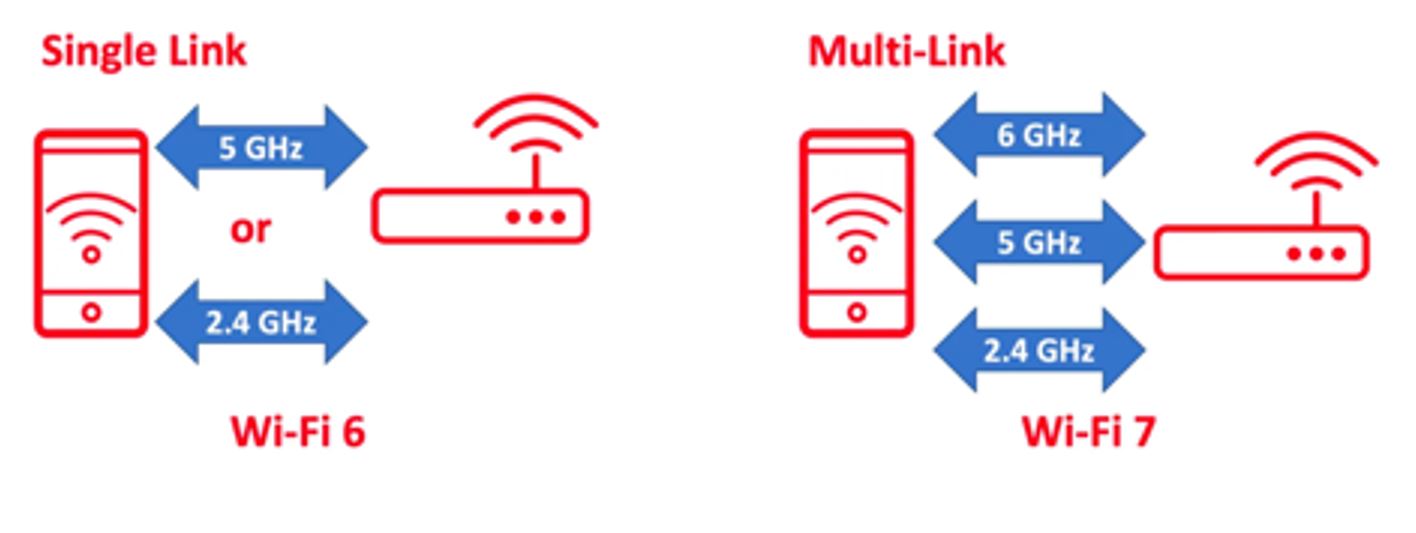
Fig.3. Single-link operation of Wi-Fi 6 versus MLO of Wi-Fi 7
RF Testing with signaling: Essential for Wi-Fi 7 Performance
The more advanced Wi-Fi 7 capabilities will enable growth in IoT adoption in both enterprise and household conditions. Higher IoT adoption will lead to more complex network conditions that will have a negative impact on network performance, hence worsening user experience. This is an inevitable fact of wireless technology evolution. With cellular, we have gone through this already.
One of the most effective solutions to ensure device performance under these conditions is to run RF testing with signalling. Data throughput testing is essential to confirm that devices can sustain sufficient data rates in a complex network condition. This testing is particularly vital in densely populated areas, such as stadiums, offices, factories, airports, and hospitals. The list goes on. Those places have numerous devices and different types of applications, which can lead to RF signal interference, making the identification and mitigation of such issues crucial for ensuring adequate performance.
As mentioned earlier, Wi-Fi 7 supports faster data rates, wider band channels, higher modulations, and MLO. RF tests can verify your devices and networks truly achieve and maintain these higher rates in real-world conditions. This ensures that Wi-Fi 7 devices can maintain consistent and reliable connectivity even when operating in multi-band scenarios. Additionally, Wi-Fi 7 devices need to comply with international standards and regulations for signal strength, spectrum usage, and non-interference with other services. This underscores the importance of RF testing with signalling in ensuring that Wi-Fi 7 fulfils its potential for faster, more efficient, and reliable wireless communication.
Another critical aspect of RF test with signalling in Wi-Fi 7 is managing network capacity and latency. These tests assess how the network copes with increased data loads, essential for maintaining low-latency communication in bandwidth-intensive applications like extended reality (XR) which includes augmented reality (AR), mixed reality (MR), and virtual reality (VR). Furthermore, in environments with dense wireless signals, Wi-Fi 7 devices must perform optimally without interference from other devices and networks. RF testing with signaling plays a key role in assessing devices’ ability to mitigate interference.
Impacts of Wi-Fi 7 Across Industries and Consumer Experiences

Fig. 4. Interoperability Industrial IoT of the factory floor
Wi-Fi 7 promises significant improvements for both industries and consumers. For industries, it provides the necessary resources for tasks like real-time data analytics and the operation of autonomous systems, crucial in sectors like manufacturing and logistics. Many types of machines can be integrated into the Wi-Fi network to improve efficiency, productivity, and security, as shown in Figure 4.
Consumers will enjoy enhanced daily internet experiences, with reduced buffering times and faster download speeds. Household users can add more smart devices such as switches, locks, security cameras, and home appliances to their networks without experiencing a performance decline.
With Wi-Fi 7 and 5G technologies, the adoption of customer premises equipment (CPE) may drastically increase. CPEs convert 5G cellular signals to Wi-Fi signals. With them, there will be no more wires and drilling holes around your house to get the internet to your home anymore. They will deliver a seamless transition between cellular and Wi-Fi connections. For those types of scenarios, there will be additional tests to ensure excellent performance in cellular and Wi-Fi interworking.
.
 (0)
(0) (0)
(0)Archive
- October 2024(44)
- September 2024(94)
- August 2024(100)
- July 2024(99)
- June 2024(126)
- May 2024(155)
- April 2024(123)
- March 2024(112)
- February 2024(109)
- January 2024(95)
- December 2023(56)
- November 2023(86)
- October 2023(97)
- September 2023(89)
- August 2023(101)
- July 2023(104)
- June 2023(113)
- May 2023(103)
- April 2023(93)
- March 2023(129)
- February 2023(77)
- January 2023(91)
- December 2022(90)
- November 2022(125)
- October 2022(117)
- September 2022(137)
- August 2022(119)
- July 2022(99)
- June 2022(128)
- May 2022(112)
- April 2022(108)
- March 2022(121)
- February 2022(93)
- January 2022(110)
- December 2021(92)
- November 2021(107)
- October 2021(101)
- September 2021(81)
- August 2021(74)
- July 2021(78)
- June 2021(92)
- May 2021(67)
- April 2021(79)
- March 2021(79)
- February 2021(58)
- January 2021(55)
- December 2020(56)
- November 2020(59)
- October 2020(78)
- September 2020(72)
- August 2020(64)
- July 2020(71)
- June 2020(74)
- May 2020(50)
- April 2020(71)
- March 2020(71)
- February 2020(58)
- January 2020(62)
- December 2019(57)
- November 2019(64)
- October 2019(25)
- September 2019(24)
- August 2019(14)
- July 2019(23)
- June 2019(54)
- May 2019(82)
- April 2019(76)
- March 2019(71)
- February 2019(67)
- January 2019(75)
- December 2018(44)
- November 2018(47)
- October 2018(74)
- September 2018(54)
- August 2018(61)
- July 2018(72)
- June 2018(62)
- May 2018(62)
- April 2018(73)
- March 2018(76)
- February 2018(8)
- January 2018(7)
- December 2017(6)
- November 2017(8)
- October 2017(3)
- September 2017(4)
- August 2017(4)
- July 2017(2)
- June 2017(5)
- May 2017(6)
- April 2017(11)
- March 2017(8)
- February 2017(16)
- January 2017(10)
- December 2016(12)
- November 2016(20)
- October 2016(7)
- September 2016(102)
- August 2016(168)
- July 2016(141)
- June 2016(149)
- May 2016(117)
- April 2016(59)
- March 2016(85)
- February 2016(153)
- December 2015(150)
